Businesses must weigh the pros and cons of each to determine the optimal approach. The key difference between absorption costing and variable costing lies in how fixed manufacturing overhead costs are handled. To further examine the reason income is higher, remember that $450,000 was attributed to total production under absorption costing. Under variable costing, total product costs were $300,000 and 10% ($30,000) of that amount would be assigned to inventory. Another way to view the impact of the inventory build-up is to examine the following “cups.” The top set of cups initially contains the costs incurred in the manufacturing process. With absorption costing, those cups must be emptied into either cost of goods sold or ending inventory.
Variable Cost vs. Fixed Cost: What’s the Difference?
In the context of measuring inventory and income, a manager will want to understand both absorption costing and variable costing techniques. This information must be interlaced with knowledge of markets, customer behavior, and the like. The resulting conclusions can set in motion plans of action that bear directly on the overall fate of the organization. By understanding a product’s cost composition, management can make better decisions about pricing, production levels, and other aspects of their business.
Consider your accounting system
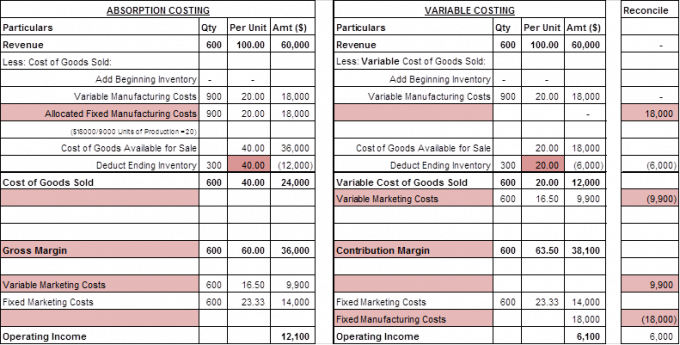
Under absorption costing, each unit inending inventory carries $0.60 of fixed overhead cost as part ofproduct cost. Therefore, ending inventory under absorption costingincludes $600 of fixed manufacturing overhead costs ($0.60 X 1,000units) and is valued at $600 more than under variable costing. Variable costing is an accounting method that includes only variable production costs—direct materials, direct labor, and variable manufacturing overhead—as product costs. Fixed overhead costs are considered period costs and are expensed in the period incurred, rather than allocated to units produced. With absorption costing, gross profit is derived by subtracting cost of goods sold from sales.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Variable Costing Method
This analysis is designed to reveal the break-even point in production by determining how many products a company must manufacture and sell to reach the point of profitability. Product and period costs are essential for management accounting because they help management make informed business decisions. Product costs are the products that a company produces, while period costs are the costs of doing business, such as administrative and marketing expenses. Similarly, period costs are essential for management accounting because they provide insights into a company’s performance. Period costs can include administrative expenses, marketing expenses, research and development expenses, and other overhead costs. Direct costing assigns the direct costs of producing a good or service to that product, while absorption costing assigns all production costs, including indirect costs, to a product.
It provides a more comprehensive cost perspective
- Direct costs are those costs that can be directly traced to a specific product or service.
- Likely, variable costing information is taken into account in making the decisions relating to these types of examples.
- Direct costing assigns the direct costs of producing a good or service to that product.
- Selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A) are classified as period expenses.
- The key differences between them relate to how fixed overhead costs are handled.
The key point here is that variable costing information is useful, but it should not be the sole basis for decision making. Ultimately, the best method of accounting for product costs depends on the company’s specific needs. However, it is important to be aware of the potential impact of absorption costing and variable costing on manufacturing decision-making. This includes direct and indirect costs, such as materials, labor, overheads, and marketing. The purpose of absorption costing is to create a full-cost accounting system that can be used to make pricing decisions. Absorption costing is a method of accounting that recognizes all manufacturing costs, including direct and indirect costs, as company expenses.

Accounting Jobs of the Future: How Staffing Agencies Can Help Land Them
Because fixed costs are spread across all units manufactured, the unit fixed cost will decrease as more items are produced. Therefore, as production increases, net income naturally rises, irs down current problems and outages because the fixed-cost portion of the cost of goods sold will decrease. The variable cost per unit is \(\$22\) (the total of direct material, direct labor, and variable overhead).
Absorption costing fails to provide as good an analysis of cost and volume as variable costing. If fixed costs are a substantial part of total production costs, it is difficult to determine variations in costs that occur at different production levels. This makes it more difficult for management to make the best decisions for operational efficiency.
Recognize that a reduction in inventory during a period will cause the opposite effect from that shown. Specifically, a portion of the contents of the beginning inventory cup would be transferred to expense commensurate with the decrease in inventory. Since the inventory cup contains less under variable costing, expect expenses to be lower and income to be higher.
